>
Ophidiiformes (Cusk eels) >
Ophidiidae (Cusk-eels) > Ophidiinae
Etymology: Lepophidium: Latin, lepus, leporis = rabbit + Greek, ophis = serpent (Ref. 45335); collettei: Named for Bruce B. Collette.
Eponymy: Dr Bruce Baden Collette (d: 1934) is an American ichthyologist. [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
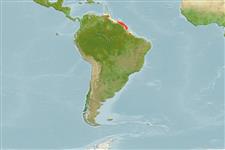
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ekologi
laut dasar (demersal); kisaran kedalaman 7 - 66 m (Ref. 91765). Tropical; 12°N - 1°S, 64°W - 45°W (Ref. 91765)
Western Atlantic: Shelf waters off the mouth of the Amazon and along the Guianan coast to the Gulf of Paria between Trinidad and Venezuela.
Size / Weight / umur
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 16.4 cm SL jantan/; (Ref. 91765)
deskripsi pendek
Kunci identifiaksi (pengenalan) | Morfologi | Morfometrik
duri punggung lunak (Keseluruhan (total)) : 116 - 122; Sirip dubur lunak: 96 - 103; vertebrata, bertulang belakang: 65 - 69. This species can be distinguished from all its congeners on the basis of vertebral counts (only Lepophidium aporrhox has fewer vertebrae than L. collettei with no overlap in number of precaudal vertebrae, 14-15 vs. 12-13 in L. aporrhox). L. collettei differs further from L. aporrhox in dorsal rays (116-122 vs. 106-115), rudiments on lower gill arch (2-7 vs. 8-12), length of the long (9-11% vs. 13-18%) and short pelvic rays (5-7% vs. 8-12%) in SL; differs from L. brevibarbe in the absence of a distally expanded anterior rib in males or haltere as seen in L. brevibarbe, developed rakers on the lower gill arch (6-8 vs. 4-5), and in having a deeper body; from L. gilmorei by the average number of caeca (5.4 vs. 3.2), total gill raker elements (12-17 vs. 8-9), dorsal fin origin (between neural spines 4-5 and 5-6 vs. between 3-4); from L. marmoratum by caudal vertebrae (51-54 vs. 55-58), short pelvic rays as a percentage of standard length (5-7% vs. 8-12%), and lack of dark spots on the head and body, in rows or otherwise; from the Pacific L. microlepis by average head length (20.8% vs. 24.3% in SL) and long pelvic rays (9-11% vs. 5-8% in SL); on the basis of dorsal rays (116-122), from L. pheromystax (125-133), L. robustum (123-126), and L. stigmatistium (123-131) Ref. 91765.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Kematangan | Reproduksi, perkembang biakan | Pemijahan | telur-telur | Fecundity | Larva
Robins, C.R., R.H. Robins and M.E. Brown, 2012. A revision of Lepophidium (Teleoastei, Ophidiidae), with descriptions of eight new species. Bulletin of the Florida Museum of Natural History 52(1):1-94. (Ref. 91765)
Status IUCN Red List (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
ancaman kepada manusia
Harmless
penggunaan manusia
Alat, peralatan
laporan khas
muat turun XML
Sumber internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 26.6 - 28, mean 27.4 °C (based on 60 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00102 (0.00046 - 0.00225), b=3.06 (2.88 - 3.24), in cm total length, based on all LWR estimates for this body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.5 ±0.7 se; based on size and trophs of closest relatives
Daya lenting (Ref.
120179): Tinggi, Waktu penggandaan populasi minimum kurang dari 15 bulan (Preliminary K or Fecundity.).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (10 of 100).