Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays) >
Orectolobiformes (Carpet sharks) >
Hemiscylliidae (Bamboo sharks)
Etymology: Chiloscyllium: cheilos (Gr.), lip, referring to membranous and broad lower lip, presumably of C. plagiosum (proposed without a species); skylion, Greek for dogfish or small shark (See ETYFish); griseum: Medieval Latin for gray, referring to light-gray coloration in spirits (usually light-brown in life) (See ETYFish).
More on authors: Müller & Henle.
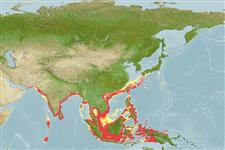
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 5 - 100 m (Ref. 106604). Tropical; 34°N - 10°S, 60°E - 150°E
Indo-West Pacific: Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Thailand. Reported records of this species from the Philippines, Taiwan, and Japan are misidentifications of
C. punctatum (Ref. 125614). Many country records need confirmation (Ref. 13575).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ?, range 45 - ? cm
Max length : 77.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 90102)
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Anal spines: 0. Genus: Nostrils subterminal on snout; pre-oral snout long, mouth closer to eyes than snout tip; eyes and supraorbital ridges hardly elevated; no black hood on head or large spot or spots on sides of body above pectoral fins (Ref. 43278). Caudal fin with a pronounced subterminal notch but without a ventral lobe (Ref. 13575).
Species: Light brown, yellow-brown or grey-brown above, cream below, with 12-13 prominent saddle marks in young, fading with growth and absent in adults (Ref. 13575). Dark bands in juveniles not outline in black (Ref. 13575). Dorsal fins smaller than pelvic fins, without projecting free rear tips (Ref. 13575). Body without lateral dermal ridge (Ref. 4832,43278, 13575).
A common inshore bottom shark (Ref. 247). Often found in estuaries (Ref. 4832). Probably feeds mainly on invertebrates (Ref. 247, 43278). Oviparous (Ref. 43278, 50449). Utilized as a food fish (Ref. 171).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Oviparous, deposits eggs in small, oval eggs cases on the bottom (Ref. 247). Paired eggs are laid. Embryos feed solely on yolk (Ref. 50449). Distinct pairing with embrace (Ref. 205). During copulation observed in captivity, the male bites the female's pectoral fin in a side-to-side position (Ref. 49562, 51121).
Ebert, D.A., S. Fowler and M. Dando, 2021. Sharks of the World: A complete guide. Princeton University Press, 607p. (Ref. 125614)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 24.9 - 29.1, mean 28.3 °C (based on 1090 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5039 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00389 (0.00183 - 0.00827), b=3.06 (2.87 - 3.25), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species & (Sub)family-body (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.7 ±0.3 se; based on diet studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (Fec assumed to be <100).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate to high vulnerability (51 of 100).