Elasmobranchi (squali e razze) (sharks and rays) >
Pristiophoriformes (Saw sharks) >
Pristiophoridae (Saw sharks)
Etymology: Pristiophorus: pristio-, presumably derived from prio (Gr.), to saw, but treated here as a noun (a saw); phorus, from phoreus (Gr.), bearer or carrier, referring to saw-like snout (note also that pristis is Greek for sawfish) (See ETYFish); japonicus: -icus (L.), belonging to: Japan, where type locality (not specified) is situated (See ETYFish).
More on author: Günther.
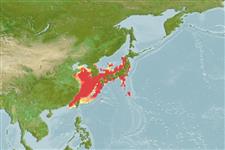
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecologia
marino demersale; distribuzione batimetrica 0 - 500 m (Ref. 54710). Deep-water; 48°N - 22°N, 118°E - 145°E (Ref. 54710)
Northwest Pacific: Japan, Korea, northern China. Does not occur in the Western Central Pacific (Ref. 31368).
Size / Peso / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 136.0 cm TL (female)
Short description
Chiavi di identificazione | Morfologia | Morfometria
Pristiophorus japonicus has a long, narrow, and narrowly tapering rostrum (rostrum length is 26-29% of TL), distance from rostral tip to barbels about equal or slightly greater than distance from barbels to mouth (1:1.1-1.2); distance from rostral barbels to nostrils about equal to distance from nostrils to 1st gill slits. About 15-26 large rostral teeth on each side of the rostrum in front of the barbels, 9-17+ behind them; distance from mouth to nostrils 1.1-1.2 times internarial space. Tooth rows 34-58 in upper jaw. Dorsal and pectoral fins covered with denticles in large specimens. Lateral trunk denticles largely unicuspidate. First dorsal fin origin behind free rear tips of pectorals by eye length or more (Ref. 247).
Caudal fin almost straight, with slender upper and lower lobes; pectoral well developed but are not ray-like (Ref. 6871).
Lives on continental shelves and upper slopes on or near the bottom. Also found in coastal waters on sand or mud bottoms. Feeds on small bottom organisms using its barbels to poke the bottom with its snout. Ovoviviparous, with 12 young in a litter.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturità | Riproduzione | Deposizione | Uova | Fecundity | Larve
Ovoviviparous, embryos feed solely on yolk (Ref. 50449).
Compagno, L.J.V., 1984. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 4. Sharks of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Part 1 - Hexanchiformes to Lamniformes. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(4/1):1-249. Rome, FAO. (Ref. 247)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Pesca: commerciale
Strumenti
Special reports
Download XML
Fonti Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 7.7 - 21.8, mean 17.4 °C (based on 199 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5156 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00389 (0.00180 - 0.00842), b=3.12 (2.94 - 3.30), in cm total length, based on all LWR estimates for this body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.8 ±0.58 se; based on food items.
Resilienza (Ref.
120179): Basso, tempo minimo di raddoppiamento della popolazione 4.5 - 14 anni (Fec=12).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (82 of 100).