Teleostei (teleosts) >
Blenniiformes (Blennies) >
Blenniidae (Combtooth blennies) > Salariinae
Etymology: Salaria: Latin, salar, salaris = trout (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Risso.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
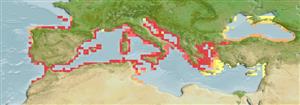
Marine; brackish; demersal. Subtropical; 46°N - 33°N, 10°W - 42°E
Eastern Atlantic: Atlantic coast from France to Morocco; also in the Mediterranean and Black seas and in the Suez Canal.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 13.8 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 118193)
Dorsal spines (total): 11 - 13; Dorsal soft rays (total): 22 - 25; Anal spines: 2; Anal soft rays: 23 - 26. Diagnosis: Mature males with well-developed head-crest and anal gland in the first two anal-fin rays; sneaker males much smaller than nesting males and do not display male secondary sexual characters (Ref. 94108).
Facultative air-breathing (Ref. 126274); Adults occur in the intertidal zone and shallow bottoms, on rocks or sand between pebbles and vegetation (Ref. 5981). Often in brackish waters down to 5 ppt (Ref. 5981). Inhabit crevices or piddock holes, males remain in cavities above water-level during low tide (Ref. 5981). Feed on benthic invertebrates, mainly mollusks, also algae (Ref. 5981). Also ingest large amounts of aquatic insects and pupae (Ref. 94105). Oviparous (Ref. 205). Mature males adopt a passive role during courtship, rarely court females, do not defend nest territory, but provide parental care to eggs. Sneaker males assume a female-like behavior in order to approach the nests of nesting males and parasitically fertilize the eggs (Ref. 94113). Eggs are demersal and adhesive (Ref. 205). Has been reared in captivity (Ref. 35421).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Males court by nodding and undulating movements and drive females to spawning place by biting and butting (Ref. 5981) though this event is rarely done by the males, more or less adopting a passive role in the courtship (Ref 94113). Additionally, males don't defend a territory around the nest (Ref. 94113) though they guard eggs from several females (Ref. 5981, 94113).
Zander, C.D., 1986. Blenniidae. p. 1096-1112. In P.J.P. Whitehead, M.-L. Bauchot, J.-C. Hureau, J. Nielsen and E. Tortonese (eds.) Fishes of the North-eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean, volume 3. UNESCO, Paris. (Ref. 5981)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-1)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: subsistence fisheries
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 15 - 21.2, mean 18.8 °C (based on 615 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5312 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01096 (0.00857 - 0.01402), b=3.00 (2.93 - 3.07), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.6 ±0.0 se; based on diet studies.
Generation time: 2.2 ( na - na) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 1
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): High, minimum population doubling time less than 15 months (K=0.50).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low to moderate vulnerability (25 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 127 [21, 405] mg/100g; Iron = 1.39 [0.52, 4.55] mg/100g; Protein = 4.16 [0.45, 7.88] %; Omega3 = 0.443 [0.183, 1.088] g/100g; Selenium = 8.2 [1.8, 25.0] μg/100g; VitaminA = 25.1 [8.9, 69.6] μg/100g; Zinc = 1.24 [0.59, 2.46] mg/100g (wet weight);