Teleostei (teleosts) >
Carangiformes (Jacks) >
Carangidae (Jacks and pompanos) > Naucratinae
Etymology: Seriola: Latin word diminutive with the meaning of a large earthenware pot (Ref. 45335).
Eponymy: Dr André Marie Constant Duméril (1774–1860) was a French zoologist who qualified as a physician (1793). [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
More on author: Risso.
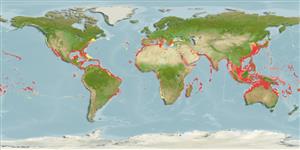
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; reef-associated; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 1 - 385 m (Ref. 11441), usually 18 - 72 m (Ref. 9626). Subtropical; 49°N - 36°S, 98°W - 128°E
Circumglobal. Tropical and warm temperate seas. Indo-West Pacific: South Africa, Persian Gulf, southern Japan and the Hawaiian Islands, south to New Caledonia; Mariana and Caroline islands in Micronesia. Western Atlantic: Bermuda (Ref. 26938), Nova Scotia, Canada to Brazil; also from the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea (Ref. 9626). Eastern Atlantic: British coast (vagrant) to Morocco and the Mediterranean. Distribution in eastern central Atlantic along the African coast is not well established due to past confusion with Seriola carpenteri (Ref. 7097).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 90.8, range 80 - 127 cm
Max length : 190 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3397); common length : 100.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3197); max. published weight: 80.6 kg (Ref. 3287); max. reported age: 15 years (Ref. 113943)
Dorsal spines (total): 8; Dorsal soft rays (total): 29 - 35; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 18 - 22. Bluish grey or olivaceous above, silvery white below; amber stripe along midside of body; fins dusky (Ref. 3197). Second dorsal and anal fins with low anterior lobe (Ref. 26938). Species of Seriola lack scutes (Ref. 37816).
Adults found in deep seaward reefs; occasionally entering coastal bays. They feed primarily on fishes such as the bigeye scad, also on invertebrates (Ref. 4233). Small juveniles associate with floating plants or debris in oceanic and offshore waters. Juveniles form small schools or solitary (Ref. 5213). Eggs are pelagic (Ref. 4233). Utilized fresh and frozen; eaten pan-fried, broiled and baked (Ref. 9987). Reported to cause ciguatera in some areas (Ref. 26938).
Spawning happens during the summer, in areas near the coast. Embryo development lasts about 40 hours at 23° and larval development 31-36 days. Egg size 1.9 mm, larval at hatching 2.9 mm.
Paxton, J.R., D.F. Hoese, G.R. Allen and J.E. Hanley, 1989. Pisces. Petromyzontidae to Carangidae. Zoological Catalogue of Australia, Vol. 7. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, 665 p. (Ref. 7300)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes; aquarium: public aquariums
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 16.9 - 29, mean 27.1 °C (based on 3486 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5020 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01778 (0.01360 - 0.02326), b=2.91 (2.83 - 2.99), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.0 se; based on diet studies.
Generation time: 5.5 (3.9 - 5.8) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 11
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (K=0.18; tm=4; tmax=15).
Prior r = 0.48, 95% CL = 0.32 - 0.72, Based on 1 full stock assessment.
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate to high vulnerability (54 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): High vulnerability (62 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 15 [7, 27] mg/100g; Iron = 0.641 [0.347, 1.180] mg/100g; Protein = 19.9 [16.9, 22.6] %; Omega3 = 0.238 [0.141, 0.418] g/100g; Selenium = 31.8 [16.4, 60.8] μg/100g; VitaminA = 62.5 [8.3, 430.9] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.351 [0.235, 0.528] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.