Myxini (hagfishes) >
Myxiniformes (Hagfishes) >
Myxinidae (Hagfishes) > Eptatretinae
Etymology: Eptatretus: hepta (Gr.), seven; tretos (Gr.), perforated (i.e., with holes), referring to seven gill apertures on what would later be described as Homea banksii (=E. cirrhatus) [range within genus is 6-14 pairs of gill apertures] (See ETYFish); grouseri: In honor of McMillan’s son, David “Grouser” McMillan, a Chief Engineer in the U.S. Merchant Marine, for “continued encouragement” of Mom’s hagfish studies and for his knowledge and love of ships and the sea (See ETYFish).
Eponymy: David ‘Grouser’ Allen McMillan (d: 1957) is a Chief Engineer in the US Merchant Marine and the author’s son. She honoured him in the name for his: “…continued encouragement of Mom’s hagfish studies and for his knowledge and love of ships and the sea.” (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
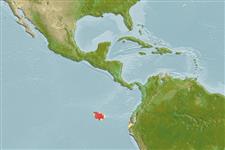
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; bathydemersal; non-migratory; depth range 648 - 722 m (Ref. 55621). Deep-water
Southeast Pacific: endemic in Galapagos Islands.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 37.8 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 31788)
Short description
Identification keys | Morphology | Morphometrics
This species is distinguished from its congeners except E. aceroi, E. profundus, E. wandoensis, E. wayuu by the number of gill apertures arranged in a straight line, 5 pairs (6 in one specimen of E. grouseri); 3/2 multicusp pattern of teeth; differs from these five-gilled congeners by having: total cusps 44-48 (vs. 58 in E. aceroi, 40-43 in E. wandoensis, 41-43 in E. wayuu); prebranchial pores 11-12 (vs. 44 in E. aceroi, 14-18 in E. wandoensis, 24 in E. wayuu); trunk pores 42-48 (vs. 107 in E. aceroi, 48-51 in E. profundus, 38-40 in E. wayuu); tail pores 13-15 (9-11 in E. wandoensis); total pores 71-79 (vs. 174 in E. aceroi, 81-86 in E. profundus) (Ref. 123790).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Copulatory organ absent. The gonads of hagfishes are situated in the peritoneal cavity. The ovary is found in the anterior portion of the gonad, and the testis is found in the posterior part. The animal becomes female if the cranial part of the gonad develops or male if the caudal part undergoes differentiation. If none develops, then the animal becomes sterile. If both anterior and posterior parts develop, then the animal becomes a functional hermaphrodite. However, hermaphroditism being characterised as functional needs to be validated by more reproduction studies (Ref. 51361 ).
McMillan, C.B., 1999. Three new species of hagfish (Myxinidae, Eptatretus) from the Galápagos Islands. Fish. Bull. 97:110-117. (Ref. 31788)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: of no interest
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 6.9 - 11.2, mean 9.5 °C (based on 7 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00204 (0.00094 - 0.00444), b=2.93 (2.74 - 3.12), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.1 ±0.7 se; based on size and trophs of closest relatives
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (Fec assumed to be <100).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low to moderate vulnerability (28 of 100).