| Gempylidae (Snake mackerels) |
| 52 cm SL (male/unsexed) |
|
bathypelagic; marine; depth range 0 - 2830 m |
| Southern Ocean: circumpolar. In the belief that there was only a single species of Paradiplospinus, many authors used the name Paradiplospinus gracilis as including Paradiplospinus antarcticus. |
|
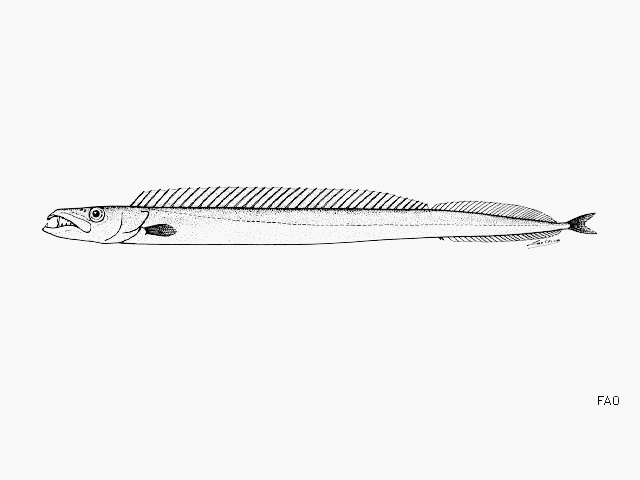
Dorsal spines (total): 36-39; Dorsal soft rays (total): 24-34; Anal spines: 2-2; Anal soft rays: 25-31; Vertebrae: 64-67. Body is extremely elongate. Mouth with fang-like teeth, 3-6 fangs anteriorly in upper jaw and 1 fang on each side of the lower jaw. Pyloric caeca 6. Color is silvery white without any conspicuous marks except 40 - 50 narrow longitudinal lines of pale melanophores; the dorsal-fin base, opercular region and caudal-fin origin dark brownish. |
| Adults and subadults epipelagic to mesopelagic, or mesobenthopelagic at shelves and slopes from surface to 830 m (temp. 0° to 4°C). Larvae and juveniles, probably mesopelagic to bathypelagic, down to 2,830 m depth (Ref. 5084). Feeds on krill, squid and fishes (predominantly myctophids). Larval and juvenile specimens mostly obtained between southern land masses and the Antarctic continent. |
|
Not Evaluated (N.E.) Ref. (130435)
|
| harmless |
Source and more info: www.fishbase.org. For personal, classroom, and other internal use only. Not for publication.